SECONDARY CONTAINMENT (COAXIAL) GAS PIPING
- 02 Sept 2024
Secondary containment gas piping is a specialized piping system used to transport hazardous gases safely. This system consists of two concentric pipes: an inner pipe that carries the gas and an outer pipe that provides secondary containment. The primary purpose of the outer pipe is to contain any leaks from the inner pipe, thereby preventing the release of hazardous gases into the environment and ensuring safety>
PURPOSE OF COAXIAL PIPING
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the risk of gas leaks, protecting employees and the environment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps to meet stringent safety and environmental regulations. Secondary containment may be used on any system if deemed appropriate by the authority responsible for the system.
- Flammable Gases storage licensing is managed by Singapore Civil Defence Force (SCDF) and Hazardous (Toxic & Corrosive) gases storage licensing is managed by The National Environmental Agency. (NEA).
- Leak Detection: Allows for continuous monitoring and early intervention in case of leaks..
Secondary piping containment systems available in PVC, Polypropylene, PVDF and Halar in sizes from 1” to 10” (carrier pipe size). Secondary containment systems prevent spills from aggressive chemical piping systems. This provide complete system containment including pipe, fittings and valves. The secondary containment system “must have sufficient capacity to contain at least 10% of the total volume of the primary containers or 100% of the volume of the largest container, whichever is greater.
Total Process Systems (TPS)Pte Ltd
SEMI GUIDE FOR SECONDARY CONTAINMENT OF HAZARDOUS GAS PIPING SYSTEMS
SEMI provide a guide for design, fabrication and operation of secondary contained distribution piping for hazardous production material (HPM) gases.
Secondary containment should be mandatory for all HPM’s that are included in the following categories
- Any HPM’s which have a material hazard index (MHI) value equal to or greater than 500,000.
- Highly toxic Gases.
- Pyrophoric Gases.
- Material with an NFPA 704 reactivity rating of 3 or 4
- Corrosive Gases.
- Where piping containing HPM’s is installed in a manner to conceal if from view.
- Where piping containing HPM’s is installed in adequate air change. (Not adequate fresh air).
CONTAINMENT METHODS
- Use readily available COAXIAL piping system in the market.
- Pressure Decay method (Closed secondary containment system).
- The method of detection of leakage through pressure loss, over a period of time within a piping system. Annular space is pressurised with N2, and pressure is monitored in the Gas System. Use this method for pyrophoric gases.
- Vacuum Decay method (Closed secondary containment system)
- Leakage detection determined by the loss of vacuum.
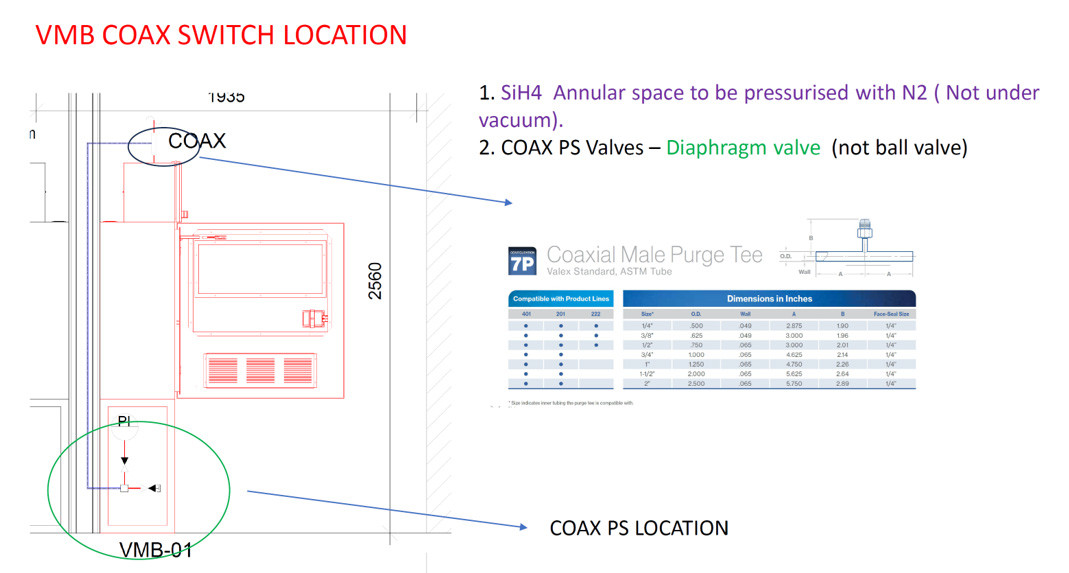
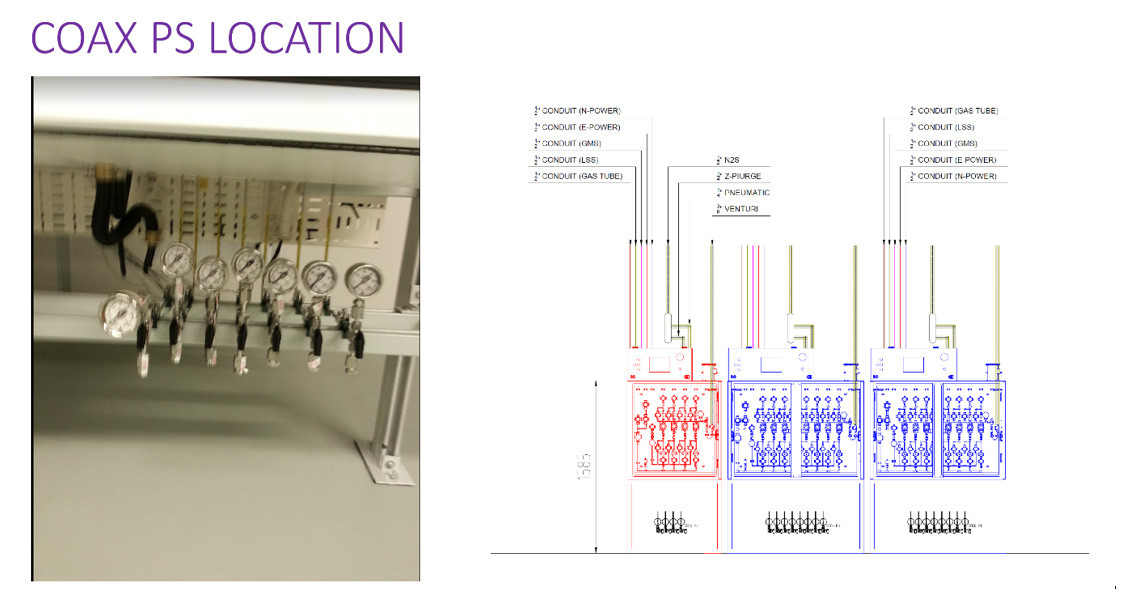
LOCATION OF COAX PRESSURE SWITCH
CODE COMPLIANCE
- SCDF Fire Code 2023.
- Workplace Safety and Health Act
- NFPA55: Compressed Gases and Cryogenic Fluids Code
- Insurance Company safety requirements
- NFPA 318: Standard for the Protection of Semiconductor Fabrication Facilities
- FM Data Sheet Semiconductor Fabrication Facilities. (7-7)
Besides complying to the codes and standards, Hazardous Gas Piping Systems design additional risk reduction measures to reduce the risk to ALARP level.
The TPS perspective on risk mitigation in semiconductor hazardous gas distribution systems is shown below. The design of Gas Systems must undergo 30%, 60%, and 90% design review alignment with the customer. The following needs will be examined and discussed during the design phase..
- NEA/SCDF Gas Storage & licencing requirements.
- QRA compliance requirements
- Customer Insurance requirements.




