BASIS OF DESIGN -BULK AMMONIA (NH3) STORAGE AND SUPPLY
- 16 Jul 2024
Ammonia (NH3) is a versatile chemical in semiconductor fabrication, used for cleaning, etching, deposition, doping, and pH control. Its effective use requires careful management to ensure both operational efficiency and safety.
TPS provides a total solution for design, QRA, HAZOP, authority submission, bidding, construction management, testing and commissioning, and obtaining a NEA Hazardous substance storage gas license. Design will address day to day operation safety, reliability and worst-case release of NH3.
Total Process Systems (TPS)Pte Ltd
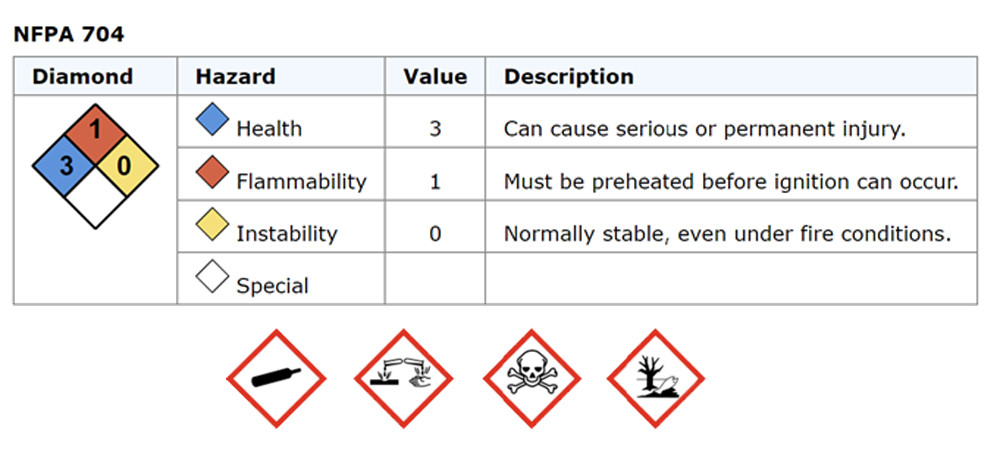
Managing the hazards of Ammonia
Ammonia is classified as a toxic, corrosive, and poisonous gas, with flammable properties. It has a Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) of 15.4% and an Upper Explosive Limit (UEL) of 25%. The Threshold Limit Value (TLV) is 25 ppm, indicating the need for strict control measures.
It is therefore important that these hazards are taken into consideration when designing Ammonia (NH3) bulk storage to ensure suitable and sufficient risk reduction measures are implemented , in line with the principle of ALARP (As Low As Reasonably Practicable)
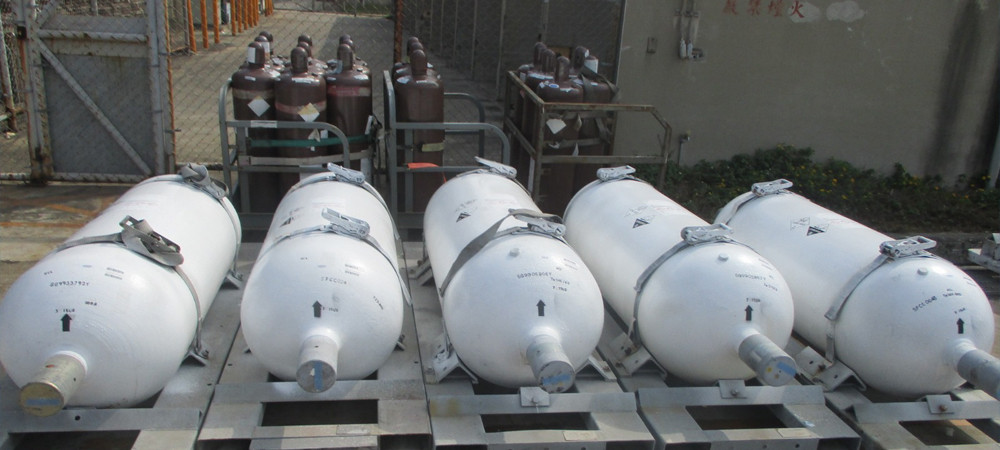
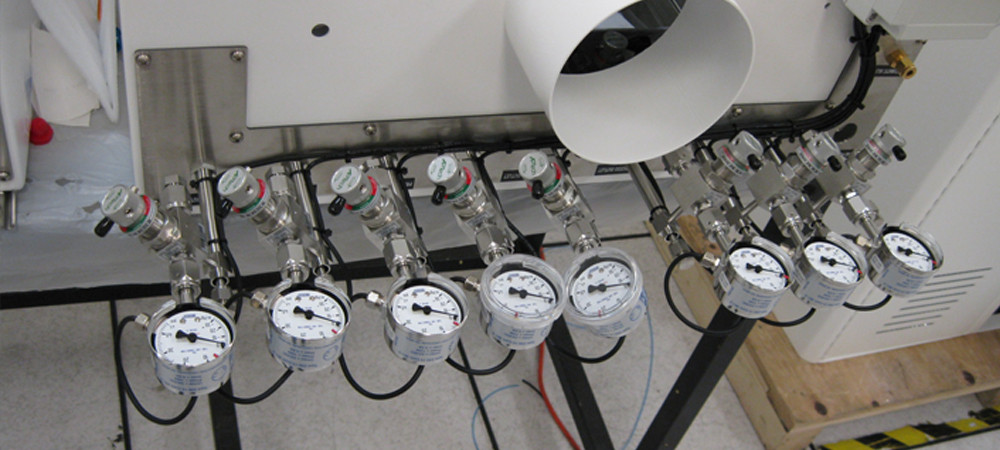
GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM
To ensure a continuous and safe supply of ammonia, TPS provides a robust gas supply system:
- System A and System B: Automatic switchover “Exhausted “ gas panels to ensure uninterrupted supply.
- System C: A backup system in case the main gas panel fails.
- Excess Flow Switch (EFS): Installed EFS at the manifold to automatically stop gas flow to detect and respond to abnormally high flow rates in gas systems.
PURGE ABATEMENT
Use purge abatement DRE 99% (TLV < 25ppm) , SEMI S2 Certified by third party such as TUV. Check abatement capability to treat the design gas flow rate below TLV level.
CIVIL , STRUCTURE & ARCHITECTURE (CSA)
Safety is paramount in our approach. The Structure architecture includes:.
- 4-Hour Fire Rated Walls: Passive fire protection on three sides thus any fires will be contained within a 4-hour fire compartment.
- 4-Hour Roller Shutter: Passive fire protection at the front.
- Closed System: To contain any potential leaks
- Retention Basin: To collect firefighting water and prevent contamination
- ESD Floor: Provide ESD floor to prevent accumulation of static electricity
FIRE PROTECTION SYSTEMS
In the event of a fire, the following systems are in place:
- UV IR Sensors: For early fire detection
- Sprinkler Protection: K80, Quick Response, activated at 68ºC.
- Manual Call Point: For immediate manual activation of the fire alarm.
- Fire Alarm System: Includes bell, strobe, and integration with the overall fire alarm systems
- Hose Reel: For manual firefighting
- Fire Extinguishers: Strategically placed for quick access.
- Fire Hydrant: Ensuring a reliable water source for firefighting.
LIFE SAFETY SYSTEMS (LSS) - GAS DETECTORS
Install Gas detectors to detect any potential loss of containment in the event of a gas leak. The Gas detectors are generally located at the Gas manifold exhausted enclosures and Gas cylinder connections area.
Install environmental gas detectors in the gas rooms to protect employees from being exposed to gas and to alert workers should a leak spread into the work areas
Install Visual and audible alarms, and the Public Address (PA) system to initiate emergency response team (ERT) to investigate life safety alarms. NH3 Gas detectors warning alarm set at 1/2 TLV (TLV:25ppm) and immediate automatic shutdown shall be set at 25ppm.
LIFE SAFETY SYSTEMS- EMO
In case of emergency, Provide Emergency Off (EMO) system to shut down the gas supply the following levels via the Emergency Off (EMO) system
- Local EMO – EMO is provided at Gas Supply Manifold.
- Room EMO – To shut down the Gas Supply from particular Room.
- Master EMO – To shut down all the Gas Supply from the Building
- Shutdown from Life Safety Systems SCADA
ELECTRICAL
- Ex-Proof Electrical Fittings.
- Earthing System for Gas Y Ton Cylinder.
DISTRIBUTION PIPING
- Use COAX Distribution lines since Ammonia (NH3) is corrosive and toxic.
SCRUBBER EXHAUST
For an Ammonia gas Y-ton failure, the contaminated gas room air will be directed to the NH3 scrubber at the rooftop before venting to atmosphere. The outlet of the scrubber is to be maintained below < 109ppm. Minimum ACH for the Ammonia room is 20 and the room is maintained at negative pressure.
Provide adequate air change for NH3 Storage room to keep the flammability limit of the gas below LEL.
- Ducting Material FM Approved ETFE
- Provide N+1 Exhaust Fan
- Emergency Power Source for Fan
- Provide water based Scrubber to treat NH3 leak during cats
CODE COMPLIANCE
- SCDF Fire Code 2023
- SS 593 Code of Practice on Pollution Control
- NEA Pollution Control /NEA Emission limit – 109 ppm
- NEA Transport Approval
- BCA
- Insurance Company safety requirements
- NFPA 55: Compressed Gases and Cryogenic Fluids Code
- NFPA 318: Standard for the Protection of Semiconductor Fabrication Facilities
At Total Process Systems (TPS) , our comprehensive solutions for ammonia management in semiconductor fabrication not only enhance operational efficiency but also prioritize the safety of your facility and personnel. By integrating advanced safety features and rigorous management protocols, we ensure that ammonia's versatile capabilities are harnessed in the safest manner possible.





