BASIS OF DESIGN -SEMICONDUCTOR CLEANROOM WET SPRINKLER SYSTEMS)
- 19 Aug 2024
A typical semiconductor facility consists of Level 1, Clean Sub Fab at Level 2 , Cleanroom at Level 3. This blog lists out the criteria for cleanroom area wet sprinkler fire protection systems. In order to prevent rework and compliance problems, it is almost necessary to have 90% of the design documents approved by the Singapore Civil Defence Force (SCDF) (Notice of Approval) and insurance firms before contracting the contractor.
The general statistics that are available from the FM data sheet show that during the operational phase of a fab, fires and explosions account for most event-based losses. Liquid damage, particularly from leaking sprinkler systems, accounts for the highest amount of asset loss.

TPS provides a total solution for Fire Systems design, authority submission, bidding, construction management, testing and commissioning, and obtaining SCDF Notice of Approval.
Total Process Systems (TPS)Pte Ltd
HAZARD
Fire safety design will go through a 30%, 60%, or 90% design review with the client facility team and client insurance company. A qualified person (QP) will review the fire design documents, such as the BOD, schematic, and layout, and submit them to SCDF for approval before appointing the fire contractor and starting the installation works.
Cleanroom area wet sprinkler system design should list out the following:
- Hazard classification (Design Density and design area)
- Sprinkler Type, Sprinkler spacing and sprinkler coverage area.
- Piping Material, Fittings and installation method.
- Sprinkler water Demand and water tank capacity.
CLEANROOM FIRE HAZARD CLASSIFICATION
In cleanrooms, fire classification is crucial due to the highly controlled environment and the potential presence of flammable gases (H2) ,pyrophoric gases (SiH4) and flammable liquids (IPA)
Automatic sprinklers for cleanroom area shall be hydraulically designed for a density of 8.2mm/min over a design area 280 sqm as per NFPA 318/NFPA 13 .
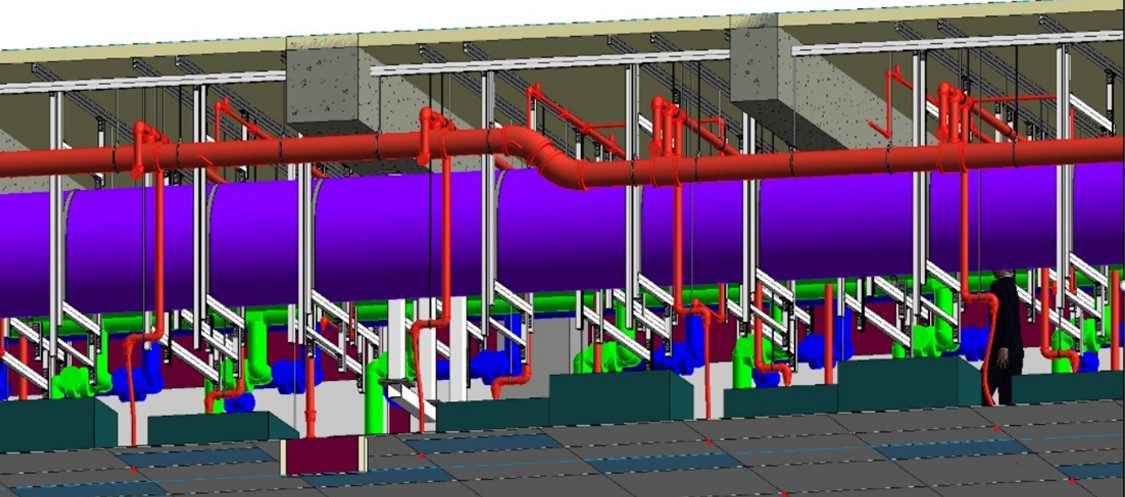
Design & install automatic sprinkler protection in the air plenum area, cleanroom space and below the raised floor.
Minimum discharge shall be 76 L/min per sprinkler from the five hydraulically most remote sprinklers [NFPA 13.26.23.3.1, NFPA 318:11.2.1.2.1]
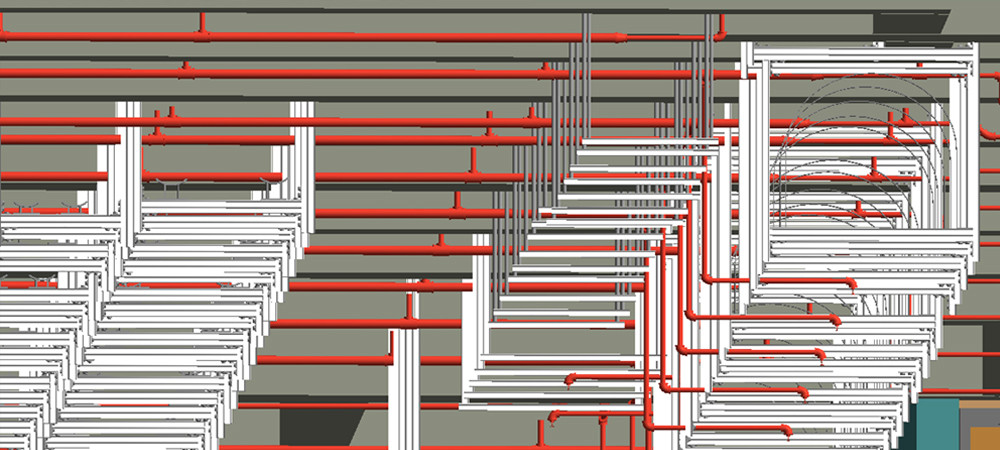
SPRINKLER COVERAGE
Design the sprinkler area coverage :9sqm sprinkler spacing 3m x 3m Typical sprinkler arrangement 3m x 3m (9sqm) below the raised floor.

SPRINKLER COVERAGE /SPRINKLER PIPING AT AIR PLENUM

SPRINKLER
Typical sprinkler use in semiconductor facilities > Quick Response Sprinkler, K80, 68°C. Use the automatic sprinkler that is FM/UL approved. Also obtain the approval from the insurance company.
WATER DEMAND
Determining water demand is critical for designing effective fire protection systems. It ensures that a facility has an adequate water supply to handle potential fire emergencies. The fire water demand is calculated by hydraulic calculation. A typical sprinkler Water Demand is 3820 L/min. Minimum residual pressure 1.4 Bar, Minimum water supply duration is 60 mins (based on Singapore Standard CP52). NFPA 13 requirements are 2 hrs. Water demand, residual pressure and water tank capacity and duration are to be discussed with the client, insurance company and submitted for SCDF approval.
CONTROL VALVE ZONING
The maximum floor area on any one floor to be protected by one control valve.
- Ordinary Hazard – 4830 sqm ( NFPA 13)
- Extra Hazard – 3720 sqm (NFPA13)
Note : Singapore Standard CP 52 allows 9000 sqm per one control valve zone for light and ordinary hazard installations.
PIPING MATERIAL
Fire sprinkler pipes and fittings are crucial components in fire suppression systems, and their material selection is vital for both safety and functionality.
- Use only FM/UL approved material & fittings
- Pipe – Internal Black steel – ASTM A53 ERW CLASS B Sch40
- External pipe – surface treated to SA 2.1/2 + Epoxy coated ( three coat -200DFT)
Grooved Couplings: Used for quick and secure connections for DN 32 and above. They allow for flexibility and easy maintenance. Use only UL/FM approved grooved couplings.
CODE COMPLIANCE
TCS is a pyrophoric and reactive liquid. Safety is paramount in our approach. The Structure architecture includes:
- SCDF Fire Code 2023
- Singapore Standard CP 52-Code of practice for automatic fire sprinkler system
- FM Data Sheet – Installation Guidelines for Automatic Sprinklers
- Insurance Company safety requirements
- NFPA 318: Standard for the Protection of Semiconductor Fabrication Facilities
- NFPA 13 : Standard for the installation of Sprinkler Systems
At TPS, we develop fire protection plans that include the layout and specifications for fire suppression systems (like sprinklers and fire extinguishers), fire alarms, and emergency exits. The fire protection design meets local, and national fire codes and standards, such as those set by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) or the International Building Code (IBC).